Computing
“Coding, it's an endless process of trial and error, of trying to get the right command in the right place, with sometimes just a semicolon making the difference between success and failure. Code breaks and then it falls apart, and it often takes many, many tries until that magical moment when what you're trying to build comes to life.” - Reshma Saujani, Entrepreneur, founder of Girls Who Code
Subject Leader: Ruth Wogan
Link Governor: Marcy Gwanzura-Nyakunengwa
As a society, we are increasingly reliant on being comfortable with the use and understanding of computers. Not all of us will work in the field of computing but technology is an integral part of our lives. The wide range of applications available to us makes computing a truly cross curricular subject. Computing can be hands on, it can be inspiring, creative and fun and it can breed resilience. It develops problem solving skills, and it opens a student’s eyes to the digital world. This can engage, enthuse and cause a real spark in students. At Christ Church, children from year 2 to year 6 have access to their own chromebook to enhance their learning across the curriculum. Children across the school reported enjoying using devices in school and at home and found lessons where technology was used to be more enjoyable and stimulating.
By teaching children to be digitally literate, students feel confident and safe online and are excited to take on the challenge of something new.
What Children Learn
Within the early years, the children are first taught how to keep themselves safe and well whilst using ICT. This includes teaching them what to do if they see something that upsets them on the internet and also to ensure that they understand their responsibilities whilst online. The children use familiar electronic devices in order to take photos or videos of their creations. The children have access to computing devices such as Ipads and Chromebooks in order to complete simple games and use simple programmes. An example of this is using a paint programme in order to create a self-portrait.
At Christ Church, the computing curriculum is split into three strands:
- Information Technology
- Digital Literacy, and
- Computer Science.
The curriculum is organised to ensure that children’s skills and knowledge progress from year to year. We use two schemes of work to teach explicit skills.
Here are some videos (video 1 and video 2) of the children sharing their thoughts about our lessons.
Our Digital Literacy/ e-safety lessons come from Project Evolve and teach children how to manage the risks of a life online. We start the Autumn term with an in-depth exploration of e-safety relevant to the children’s stage of learning. Throughout the rest of the year, we drip feed the curriculum through starters and plenaries in our computing lessons and through our PSHE lessons.
Curriculum overview for digital literacy:
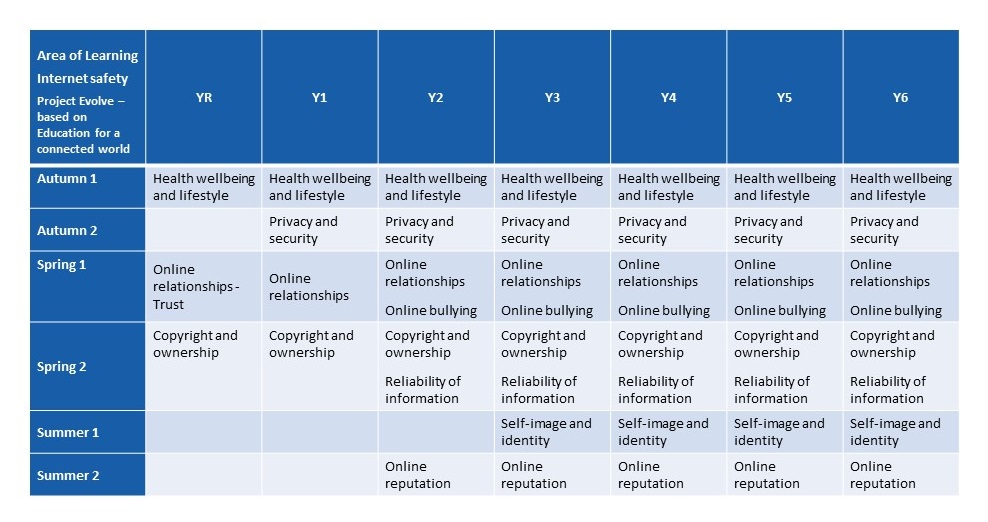
Lessons are linked to the SRE curriculum and also are linked to the UN convention on the rights of the child.
Information Technology
This is where children learn to use a range of technologies and software to achieve different goals. This could be creating a presentation to support learning in any of the foundation subjects or creating a vlog or blog about a particular issue or subject. Other examples might be creating a piece of art using the chromebook or making and editing a video to explain the impact of cyberbullying. Children learn to store and share information appropriately on the school and wider networks.
The skills to achieve the objectives for this strand of the curriculum are not always taught explicitly in a computing lesson, but are acquired in other areas of the curriculum.
Summary of Computing Coverage from Year 1 - Year 6
|
Year 1 |
Year 2 |
Year 3 |
Year 4 |
Year 5 |
Year 6 |
|
|
Autumn Term |
All year groups - E-Safety/ SRE lessons - Autumn 1 (objectives to be revisited throughout year) |
|||||
|
Spring Term |
Cross curricular learning |
|||||
|
Summer Term |
Unit 1.1 |
Unit 2.1 Unit 2.2 |
Unit 3.1 Unit 3.2 |
Unit 4.1 Unit 4.2 |
Unit 5.1 Unit 5.2 |
Unit 6.1 Unit 6.2 |
A more detailed overview of the curriculum can be found here: Computing
Digital Literacy
First and foremost, children are taught how to be safe when working online. At the start of each academic year, children explore the challenges of e-safety - learning how to recognise online dangers, address risky behaviour, and where to get help in order to stay safe. These lessons are explicitly taught in Autumn 1 and are closely linked to the SRE curriculum as well as the UN Rights of the Child. Lessons are made accessible to all children through a range of activities, including role playing, hands on and differentiated tasks. The curriculum reflects the increased exposure to risk as the children develop and explicitly teaches skills to stay safe online.
Computer Science
These lessons develop children’s understanding that programs are a set of instructions that if followed correctly will carry out a task. In KS1 this includes writing instructions to make jam sandwiches and programming a floor robot to move around a route that the children have designed. From Year 2 onwards, children are introduced to the coding language using Scratch, which teaches them how to create basic programs to make and move a character or sprite. As their skills build, children learn to write more complex programs and in year 5, children make their own computer games. In Year 5 & 6 children also have the opportunity to use Micro Bit devices which they can code to perform different tasks. You can find more about them here.
From Year 2 onwards, children cover 2 units - learning the coding skills in the first instance, and how to troubleshoot and debug programs in the second unit.
